Getting Started: What is GitLab?
GitLab is an open-source end-to-end software development platform with built-in version control, issue tracking, code review, CI/CD, and more. Self-host GitLab on your own servers, in a container, or on a cloud provider. GitLab is a DevOps software package that combines the ability to develop, secure, and operate software in a single application. Simply explained, GitLab is another DevOps tool/platform in the market which manages the complete DevOps workflows.
GitLab: an online platform relying on Git and designed for organizations
While Git can be used directly on each user’s computer — via the computer’s terminal or a Git GUI client like Sublime Merge for example — GitLab is an online platform where all actions can be done in your browser. As described on GitLab’s website, it is “an open-source software to collaborate on code”. Creating a GitLab account is free, so if you use it in a corporate context the project’s administrator will add you to the company’s relevant project(s). This means that you can potentially work on GitLab with the same account for professional projects as well as for personal projects (depending on the email address you use to create your account).
Most actions that can be done using Git on your computer can be done as well in GitLab. This is particularly key here because this means that GitLab allows non-developers—at least people who never learned how to use a version control system, like myself one year ago — to add modifications in the code without having to follow an extensive training in computer science.
In addition, GitLab presents itself as “the complete DevOps platform” because it allows much more for organizations than simply tracking the changes done by users in the main code. GitLab also includes tools to test piece of code and allow code’s deployment into production (when the code is actually applied and used by external tools relying on it). I will not go into further details here, as I want to present to main features of GitLab for beginners in the software development world.
GitLab as a DevOps platform -
- GitLab strives to become a complete DevOps platform.
- A platform on which you can build your complete DevOps workflows.
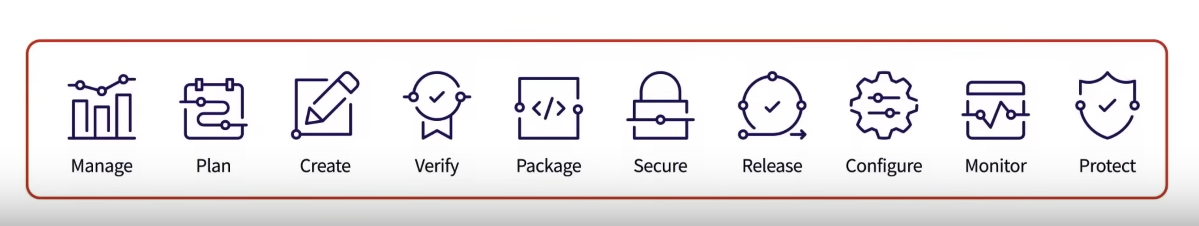
Use GitLab to -
- Set up your organization.
- Organize work with projects.
- Plan and track work.
- Build your application.
- Secure your application.
- Deploy and release your application.
- Monitor application performance.
- Monitor runner performance.
- Manage your infrastructure.
- Analyze GitLab usage.
GitLab CI/CD
CI/CD is a core part of DevOps.
What is CI/CD? CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment or Continuous Delivery. It means, automatically testing, building, and releasing the code changes to the deployment environment. So that, when the developer commits a code change to the GitLab repository, GitLab will automatically execute the CI/CD pipeline that has been configured for the project to release those code changes to the end environment where the end-users can access them.
There are many other tools for CI/CD available in the market with Jenkins being the industry leader. Even I am a Jenkins user. But all tools have advantages and disadvantages. Trying out GitLab is worth a try because all workflows are managed inside GitLab itself.
How to write a CI/CD pipeline in GitLab? See resources
- The pipeline is written in code.
- Hosted inside the application’s git repository.
- The whole CI/CD configuration is written in YAML format.
- The file has to be in
.gitlabformat with a.ymlextension. - For example, we are creating a pipeline for a demo project named gitlab-ci-cd. We can name the pipeline file as
.gitlab-ci.yml. So that GitLab can automatically detect and execute the pipeline without any extra configurations from our side.
GitLab’s architecture - How does it work?
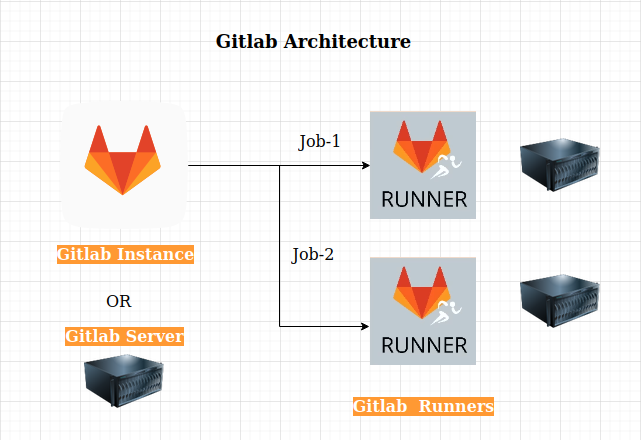
A high-level architecture can be seen here.
GitLab Instance/Server
- Host our application code, pipeline configuration, GitLab configuration, etc.
- Manage the pipeline execution.
GitLab Runners
- Agents that run your CI/CD jobs.
- GitLab server assigns pipeline jobs to available runners.
For more details on GitLab’s Architecture and its components - click here.
Benefits of GitLab
- Always keeping CI/CD and code management in the same place.
- Seamless integration into the code repository.
- Using CI/CD without the overhead of setting it up ourselves.
- Pipeline configutation as part of our application code.
- Self-hosted or SaaS managed.
Conclusion
GitLab is an easy-to-use tool for newcomers in the software development world. Indeed, its use does not require advanced knowledge of programming, as long as the user is acquainted with the programming language of the file(s) he wants to make changes on.
